| Major Groups > Cup Fungi > Helvella solitaria |

|
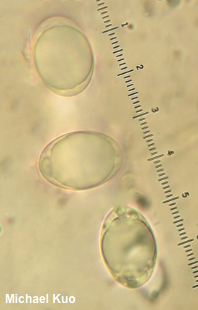
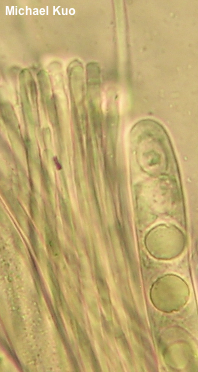
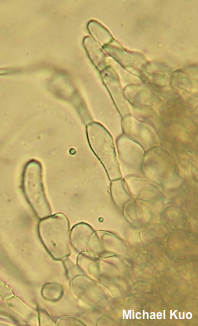
Helvella solitaria [ Ascomycota > Pezizales > Helvellaceae > Helvella . . . ] by Michael Kuo Helvella solitaria has a grayish brown to brown, cuplike cap that sits atop a whitish, deeply ribbed stem. The ribs have rounded edges and do not extend more than a few millimeters onto the undersurface of the cup, which helps to separate it from Helvella costifera and Helvella acetabulum, which have ribs that extend far onto the undersurface of the cap. Helvella solitaria grows under hardwoods or conifers, and is fairly widely distributed in North America. Several phylogenetic species have recently been separated from Helvella solitaria, including China's Helvella taiyuanensis (no morphological differences) and Europe's resurrected Helvella platypodia (putatively smaller and more gray); more are possible, especially once North American collections are studied more fully. Helvella queletii is a synonym. Thanks to Leighla Beteta for documenting, collecting, and preserving Helvella solitaria for study; her collection is deposited in The Herbarium of Michael Kuo. Description: Ecology: Probably mycorrhizal; growing alone or gregariously under hardwoods or conifers, often in the vicinity of well-rotted wood; spring through fall, or over winter in warm climates—but most often collected in late spring or early summer, in my experience. Originally described from Finland; widespread in Europe; in North America widely distributed from Alaska and the Maritime Provinces through Mexico; also recorded from Central America and Asia. The illustrated and described collections are from Colorado, Illinois, and Oklahoma. Cap: 2–5 cm across; 1.5–4 cm high; when young sometimes folded inward along a central axis, creating a saddle-bags shape; cuplike or saucer-like at maturity (but sometimes irregular in shape); upper surface grayish brown to brown or yellowish brown, smooth or slightly wrinkled, bald or, with a lens, finely fuzzy; undersurface pale grayish brown to whitish (sometimes darker near the margin), densely but finely fuzzy, at least with a lens. Stem: 12–65 mm long and 4–20 mm thick; often flaring to apex and/or base; deeply ribbed with 4–8 round-edged longitudinal ribs that terminate at the apex of the stem and do not continue onto the undersurface of the cap for more than a few millimeters; whitish or creamy yellowish. Flesh: Thin; brittle; white in the stem; whitish to brownish in the cap; unchanging when sliced. Odor: Not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative on all surfaces. Iron salts negative on stem surface. Microscopic Features: Spores 17–22 x 10–15 µm; ellipsoid; smooth; with one large central oil droplet that often nearly completely fills the spore; hyaline in KOH or water; inamyloid. Asci 175–250 x 12.5–17.5; 8-spored; tips not bluing in Melzer's. Paraphyses exceeding the asci 10–25 µm; filiform with rounded to clavate or subclavate apices; 3–6 µm wide at apex; sparingly septate; hyaline in KOH or water. Excipular surface a turf of elements 5–15 µm wide; arranged in trichoderm-like chains; frequently septate, with occasional constrictions at septa; terminal cells clavate or irregularly swollen; hyaline in KOH or water. REFERENCES: P. A. Karsten, 1871. (Seaver, 1942 [P. platypodia]; Kempton & Wells, 1970; Smith Weber, 1972; Harmaja, 1977; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Arora, 1986; Abbott & Currah, 1997; Barron, 1999; Landeros et al., 2012; Landeros et al., 2013; Beug et al., 2014; Kuo & Methven, 2014; Landeros et al., 2014; Desjardin, Wood & Stevens, 2015; Gminder & Böhning, 2017; Skrede et al., 2017; Læssøe & Petersen, 2019; Wang et al., 2019; Skrede et al., 2020.) Herb. Kuo 05099505, 06030401, 05070702, 08120708, 04211203, 05251301, 05231806, 05182101, 04172201. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2022, July). Helvella solitaria species cluster. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/helvella_solitaria.html |