|
Sycamore (Plantanus occidentalis) [ Trees > Hardwoods . . . ] Forest Type: Multiple; Riverine & Swamp
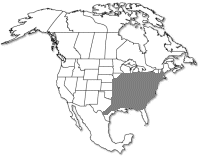
by Michael Kuo Habitat: Usually on moist soil in bottomlands; often growing with Eastern Cottonwood; often planted in urban areas; growing east of the Great Plains. Stature: 70-100+ feet high; to 8 feet in diameter; with a long main trunk. Leaves: 4-7 inches long; with 3-5 pointed lobes; coarsely toothed; bright green above; paler below. Bark: Thin, scaly, and reddish brown near the base of the tree; peeling away in plates above to reveal the white inner bark. Fruit: A hairy ball; to 1 1/2 inches long. Sources: Preston, R. J. (1989). North American Trees. Ames: Iowa State UP; Mohlenbrock, R. H. (1978). Forest Trees of Illinois. SIU: Ill. Dept. Natural Res.; Peattie, D. C. (1991). A Natural History of Trees of Eastern and Central North America. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. Frequent Mushroom Associates: Marasmius felix; Polyporus squamosus; Rhodotus palmatus; Gyromitra caroliniana; and many other mushrooms typical of eastern riverine hardwood ecosystems. Morel Hunters often swear they find Yellow Morels under sycamores and Eastern Cottonwood in riverbottoms and creek beds. Further Online Information: Sycamore USFS Fact Sheet (PDF file) |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2005, August). Sycamore (Plantanus occidentalis). Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/trees/plantanus_occidentalis.html |