| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Marasmioid > Marasmius felix |

|
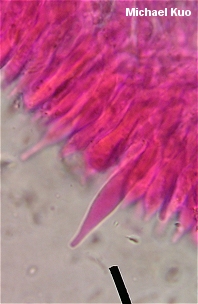
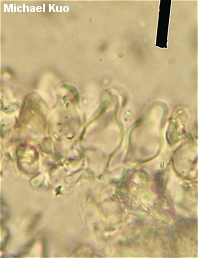
Marasmius felix [ Basidiomycetes > Agaricales > Marasmiaceae > Marasmius . . . ] by Michael Kuo If you have picked this tiny mushroom in the woods and brought it home for identification without paying much attention to your surroundings or thinking about the mushroom's ecology, you're not going to have much luck identifying it without a microscope and lots of patience. However, if you know that you were picking mushrooms in cottonwood-sycamore lowlands, and you noticed that the mushrooms were growing from the petioles of fallen sycamore leaves, identifying Marasmius felix is a cinch, since this appears to be its only ecological milieu. How cool is that? The sycamore, which reaches heights of over 100 feet, has evolved with Marasmius felix, which reaches heights of about 80 millimeters! Aside from the association with decaying sycamore leaves, distinguishing features for Marasmius felix include the tiny whitish to pink cap, the thin and wiry stem, and microscopic features (see below). Doyle & Sundberg (1989) note that Marasmius felix can often be discovered in cold weather, since it grows on year-old sycamore leaves that are often covered by the current year's leaves, which apparently provide protection from the elements. Description: Ecology: Saprobic on fallen leaves of sycamore trees (usually on leaves from the preceding year); growing alone or gregariously from petioles or major veins; summer, fall, and winter (see comments below); probably to be expected throughout the range of the tree (east of the Great Plains, south of the Great Lakes). Cap: 1.5-8 mm across; convex, becoming planoconvex; usually pleated by maturity; often somewhat wrinkled; dry; at first nearly white, becoming pinkish or pale pinkish brown with age. Gills: Attached to the stem, often by means of a collar that may or may not completely encircle the stem; distant; whitish or faintly pinkish. Stem: 10-85 mm long; less than 1 mm thick; equal; dry; wiry; sometimes slightly hairy; inserted directly into the leaf; translucent near apex, brownish to blackish brown below; occasionally branched. Flesh: Thin; insubstantial. Odor and Taste: Taste mild; odor not distinctive. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 8-8.5 x 3-3.5 µ; smooth; fusiform-ellipsoid. Pleuro- and cheilocystidia fusoid to fusoid-ventricoe, with or without a small mucro or capitate apex; thin-walled; smooth; to about 50 x 10 µ. Pileipellis hymeniform; terminal elements variously shaped (pyriform, clavate, or occasionally cystidioid). REFERENCES: >Morgan, 1906. (Saccardo, 1912; Kauffman, 1918; Gilliam, 1976; Doyle & Sundberg, 1989.) Herb. Kuo 09230607. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2013, January). Marasmius felix. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/marasmius_felix.html |