| Major Groups > Jellies > Phaeotremella frondosa |

|
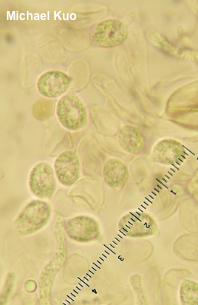
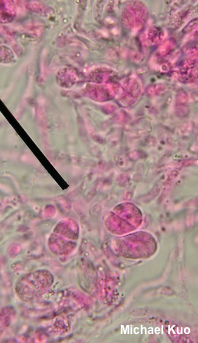
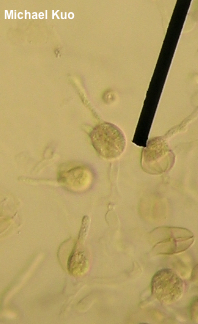
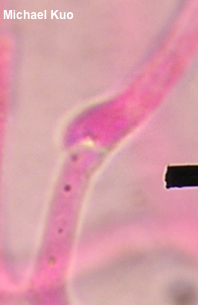
Phaeotremella frondosa [ Basidiomycota > Tremellales > Phaeotremellaceae > Phaeotremella . . . ] by Michael Kuo Associated with Stereum complicatum and other Stereum species found on the wood of hardwoods, this well-known jelly fungus is fairly easily identified on the basis of its brown color and its well-developed individual lobes, which are more "foliate" (leaf-like) than "cerebriform" (brain-like), in Mycologese. Concepts and names for this mushroom have shifted in recent years, and it is likely that your field guide calls the species featured here "Tremella foliacea." However, Spirin and collaborators (2018) reveal that 1) Tremella foliacea isn't all that closely related to Tremella mesenterica and other core Tremella species, and 2) the hardwood-associated species in North America should be called frondosa rather than foliacea (which is found on the wood of conifers). That said, the Spirin paper relied primarily on European collections, using only a few North American frondosa collections (from British Columbia), and it may well be that more focused sampling of North American collections will result in further changes. Description: Ecology: Parasitic on species of Stereum, including Stereum ostrea and Stereum complicatum; appearing on the deadwood of hardwoods; spring through fall, or over winter in warmer climates; widely distributed in North America. The illustrated and described collections are from Illinois. Fruiting Body: A mass of loosely packed lobes, 4–20 cm across and 2–7 cm high; individual lobes 2–5 cm across and 1–2 mm thick; surface bald, moist, pale brown to medium dark brown, becoming wrinkled toward point of attachment; without a stem; flesh gelatinous, brown. Odor and Taste: Not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative on surfaces. Iron salts negative on surfaces. Microscopic Features: Spores 5–8.5 x 4–6 µm; ellipsoid, with a prominent apiculus; smooth; hyaline in KOH. Probasidia ellipsoid to subglobose. Basidia to about 20 x 15 µm; ellipsoid to subglobose; developing a longitudinal septum and 4 long, fingerlike sterigmata. Hyphae 2.5–5 µm wide; often gelatinized; septate; clamped. REFERENCES: (Fries, 1822) Spirin & V. Malysheva, 2018. (Rea, 1912; Coker, 1920; Millanes et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2015; Wedin, Zamora & Millanes, 2016 . . . "Tremella foliacea": Olive, 1947; Olive, 1951; Martin, 1952; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Arora, 1986; Breitenbach & Kränzlin, 1986; Lincoff, 1992; Horn, Kay & Abel, 1993; Chen, 1998; Barron, 1999; McNeil, 2006; Miller & Miller, 2006; Binion et al., 2008; Trudell & Ammirati, 2009; Kuo & Methven, 2014; Desjardin, Wood & Stevens, 2015; Siegel & Schwarz, 2016; Woehrel & Light, 2017; Baroni, 2017.) Herb. Kuo 08230901, 03151001, 05121401, 10031603. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2018, August). Phaeotremella frondosa. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/phaeotremella_frondosa.html |