| Major Groups > Chanterelles and Trumpets > Craterellus foetidus |

|
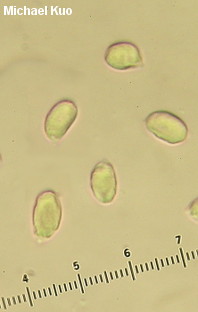
Craterellus foetidus [ Basidiomycota > Cantharellales > Cantharellaceae > Craterellus . . . ] by Michael Kuo This eastern North American mushroom is very similar to the better known "black trumpet," Craterellus fallax, but can be distinguished by the presence of fairly well developed wrinkles and folds on the under/outer surface, near the cap margin. It is also a bit more substantial than Craterellus fallax, and it tends to grow in clusters of two to four mushrooms, while Craterellus fallax only clusters rarely. Field guides emphasize a sickeningly sweet odor for Craterellus foetidus, but I have found that the heavy odor can be difficult to detect if you are not examining fresh, mature specimens. Young specimens of Craterellus foetidus, or specimens growing in very dry conditions, can be very pale, approaching whitish. This can lead to confusion, especially since the mushrooms take a relatively long time to mature (the first time I found Craterellus foetidus in this condition, I was sure I had discovered a new species). Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with oaks; growing gregariously or, more commonly, in fused clusters of 2-5 mushrooms; fairly widely distributed east of the Great Plains; late spring through early fall. The illustrated and described collections are from Illinois. Fruiting Body: 4-10 cm tall; 3-7 cm wide; thin-fleshed; shaped like an inverted vase or trumpet; the upper edge rolled under when young, becoming wavy and irregular in age; without a clearly differentiated stem and cap. Upper/Inner Surface: Color variable and dependent on conditions, but typically pale to dark watery gray (sometimes nearly white); finely, radially scaly with blackish appressed fibers and scales; the margin often blackening at maturity. Under/Outer Surface: Bald toward the base, but veined or prominently wrinkled with gill-like folds and cross-veins for the upper 1/3 of the fruiting body; gray to lilac gray (sometimes nearly white); often developing a pinkish dusting, or cinnamon to brownish stains; basal mycelium white. Flesh: Thin; gray to grayish. Odor and Taste: Odor strong and sweet in fresh, mature specimens; taste not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: Iron salts, ammonia, and KOH negative on all surfaces. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 7-10.5 x 4-5.5 µ; ellipsoid; smooth; hyaline in KOH, with ochraceous, semi-refractive contents. Basidia 4-sterigmate; 55-75 µ long. Hymenial cystidia not found. Elements of upper surface cylindric; septate; hyaline to brownish; 5-10 µ wide. Clamp connections absent. REFERENCES: A. H. Smith, 1968. (Bigelow, 1978; Smith, Smith, Weber, 1981; McKnight & McKnight, 1987; Roody, 2003; McNeil, 2006; Kuo, 2007; Binion et al., 2008; Kuo & Methven, 2014.) Herb. Kuo 06129504, 06050302, 06200304, 07210702, 07010804. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2015, February). Craterellus foetidus. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/craterellus_foetidus.html |