| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Dark-Spored > Cortinarius > Cortinarius infractus |

|
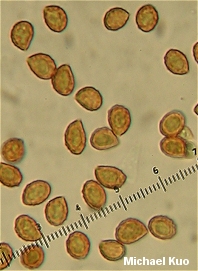
Cortinarius infractus [Basidiomycetes > Agaricales > Cortinariaceae > Cortinarius ... ] by Michael Kuo Identifying features for this fairly distinctive Cortinarius include the grayish olive to olive brown cap, the olive-tinged gills, the bitter taste, and microscopic features (including broadly ellipsoid to nearly round spores, and basidia that turn green in KOH). Cortinarius infractus is a European species that is also widely distributed in North America under both hardwoods and conifers, manifesting a fairly large range of colors--all of which suggests that there may be several North American infractus-like species waiting to be uncovered by contemporary study. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with hardwoods or (less frequently) with conifers; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously; late summer and fall (or over winter in warmer climates); widely distributed in North America. Cap: 4-10 cm; convex, becoming broadly convex to nearly flat, or broadly bell-shaped; sticky when fresh; bald; generally grayish olive to olive brown, but sometimes developing rusty to orangish brown shades. Gills: Attached to the stem; close; brownish olive to olive gray at first (sometimes with a purplish tint), becoming rusty brown. Stem: 4-9 cm long; up to about 2.5 cm thick; club shaped; dry; pale olive to whitish, discoloring brownish--or with purplish shades near the apex when young; often adorned with with rusty cortina remnants when mature. Flesh: Whitish, or with purplish shades in the stem. Odor and Taste: Odor not distinctive. Taste of cap surface bitter. Chemical Reactions: 10% KOH dark gray on cap surface; gray on flesh. 15% KOH dark gray on dried cap surface. Spore Print: Rusty brown. Microscopic Features: Spores 7-8 x 5-6 µ; subglobose to broadly ellipsoid; moderately to strongly verrucose. Basidia green in 2% KOH. Cheilo- and pleurocystidia absent; marginal cells present. Pileipellis an ixocutis of clamped elements. REFERENCES: (Persoon, 1799) Fries, 1838. (Fries, 1821; Saccardo, 1887; Kauffman, 1918; Kauffman, 1932; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1979; Moser, 1983; Arora, 1986; Breitenbach & Kränzlin, 2000; Knudsen & Vesterholt, 2008.) Herb. Kuo 09120702. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2012, January). Cortinarius infractus. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/cortinarius_infractus.html |