| Major Groups > Boletes > Xanthoconium affine |

|
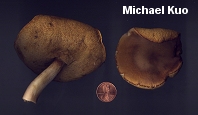
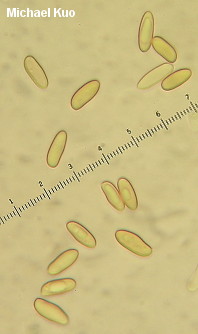
Xanthoconium affine [ Basidiomycota > Boletales > Boletaceae > Xantoconium . . . ] by Michael Kuo Formerly known as "Boletus affinis," this bolete is found in hardwood forests east of the Rocky Mountains, and in Mexico. Its spore print and mature pore surface are yellowish brown--which separates it handily from the vast hordes of boletes with olive to olive brown spores. Other defining features for Xanthoconium affine include the absence of any dramatic bruising or staining, and the fact that a drop of ammonia applied to the cap surface produces a boring, negative or faintly orangish to pinkish reaction. The chemical test helps separate it from the very similar, reddish-capped Xanthoconium purpureum, which also has yellowish brown spores but which demonstrates a green flash with ammonia. Several varieties of Xanthoconium affine have been described. Xanthoconium affine var. maculosus is more or less identical but has a cap that is spotted with whitish or pale yellow spots--while Xanthoconium affine var. reticulatum has a conspicuously reticulate stem. Boletus affinus is a synonym. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with hardwoods (especially oaks and beech) and perhaps rarely with conifers; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously; summer and fall; widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains, south to Mexico. The illustrated and described collections are from Michigan, Illinois, and Kentucky. Cap: 2-9 cm across, convex, becoming broadly convex or nearly flat; dry; very minutely velvety when in the button stage, but soon bald; brown to dark brown or yellow-brown; sometimes conspicuously spotted with whitish to yellowish spots ("var. maculosus"). Pore Surface: Whitish, becoming brownish yellow and eventually yellowish brown; not bruising, or bruising dull yellowish brown; pores circular to angular, 1-2 per mm; tubes to 5-15 mm deep. Stem: 3-8 cm long; 0.5-2 cm thick; at maturity more or less equal; solid; bald; pale at apex, streaked with a paler shade of the cap color below; not reticulate--or, in "var. reticulatum," reticulate near the apex; basal mycelium white. Flesh: Whitish throughout, unchanging when sliced, or occasionally staining slightly yellowish over time. Odor and Taste: Not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: Ammonia negative to pinkish or orangish on cap surface; negative on flesh. KOH negative to pinkish on cap surface; negative on flesh. Iron salts negative on cap surface; negative on flesh. Spore Print: Bright yellow-brown. Microscopic Features: Spores 9-14 x 3-4 µ; subfusiform; smooth; yellowish to golden in KOH. Hymenial cystidia lageniform; to about 50 x 10 µ. Pileipellis a tightly packed trichoderm with clavate or subclavate terminal elements 7.5-12.5 µ wide (an "epithelium" or hymeniform turf); hyaline to ochraceous or brownish in KOH. REFERENCES: (Peck, 1873) Singer, 1944. (Saccardo, 1888; Coker & Beers, 1943; Singer, 1947; Snell & Dick, 1970; Smith & Thiers, 1971; Grund & Harrison, 1976; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Weber & Smith, 1985; Arora, 1986; Phillips, 1991/2005; Lincoff, 1992; Metzler & Metzler, 1992; Barron, 1999; Bessette, Roody & Bessette, 2000; Roody, 2003; McNeil, 2006; Miller & Miller, 2006; Kuo, 2007; Binion et al., 2009.) Herb. Kuo 07189402, 08111203. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2015, January). Xanthoconium affine. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/xanthoconium_affine.html |