| Major Groups > Polypores > Tyromyces fumidiceps |

|
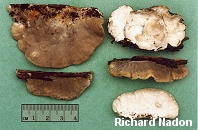
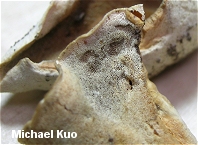
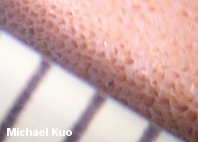
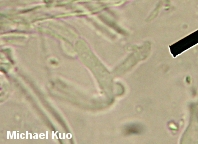
Tyromyces fumidiceps [ Basidiomycetes > Polyporales > Polyporaceae > Tyromyces . . . ] by Michael Kuo Blech. "Smoky-headed cheese fungus" is what the Greek and Latin in Tyromyces fumidiceps result in when translated into English. In this case "cheese fungus" doesn't refer to one of the many fungi associated with cheese, but a fungus with the consistency of cheese--though the modifier does dangle like a limp, cheesy polypore. Defining features for Tyromyces fumidiceps include its watery consistency, its fragrant odor, its extremely tiny pores, its buff to grayish or brownish cap surface, the tendency of the pore surface to turn greenish in old age or when dried, and microscopic features. Description: Ecology: Saprobic on the deadwood of hardwoods; causing a white rot; annual; growing alone or gregariously; often found along riverbottoms, creeks, and low-lying areas subject to floods; summer and fall; fairly widely distributed east of the Great Plains. Cap: Usually present and well developed but occasionally present merely as a folded-over edge above a spreading pore surface; up to 6 cm across and 4 cm deep; convex; semicircular to kidney-shaped; velvety to slightly hairy at first, becoming bald; off-white, grayish, smoky gray, brownish, or grayish brown; soft. Pore Surface: Whitish, becoming yellowish or pale olive in old age or when dried out; not bruising appreciably; with 4-7 angular pores per mm; tubes to 1 cm deep; tube mouths often becoming covered with crystals. Stem: Absent. Flesh: White; soft and watery when fresh. Odor and Taste: Odor fragrant when fresh; taste not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative to yellowish on cap surface and flesh. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 2.5-4 x 2-3 µ; smooth; ellipsoid to subglobose; hyaline in KOH; inamyloid. Cystidia absent, but occasional fusoid cystidioles present. Hyphal system monomitic, with conspicuous clamp connections; contextual hyphae with frequent short side branches. REFERENCES: Atkinson, 1908. (Saccardo, 1912; Overholts, 1953; Gilbertson & Ryvarden, 1987.) Herb. Kuo 09160605. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2010, March). Tyromyces fumidiceps. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/tyromyces_fumidiceps.html |