| Major Groups > Polypores > Pseudofistulina radicata |

|
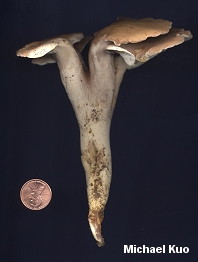
Pseudofistulina radicata [ Basidiomycetes > Agaricales > Fistulinaceae > Pseudofistulina . . . ] by Michael Kuo Pseudofistulina radicata has tubes that are discrete and clearly separated (see the illustration), like those of the well-known species Fistulina hepatica. However, Pseudofistulina radicata is a rare species, almost never treated in field guides; I have only found it once in many years of collecting mushrooms. Its distinguishing features, aside from the separated tubes, include its velvety brownish cap surface, its long and rooting stem, and the peculiar way the white pore surface terminates abruptly at the apex of the stem. Fistulina firma, Fistulina pallida, Fistulina brasiliensis, and Pseudofistulina brasiliensis are synonyms. Description: Ecology: Presumably saprobic on dead trees and stumps of oaks and chestnuts; possibly also parasitic, growing from the roots of apparently living trees (and appearing terrestrial); annual; summer and fall; known from North America east of the Mississippi, and from Central and South America. Cap: To 20 cm across; sometimes with multiple caps arising from a shared stem; irregularly shaped but typically fan-shaped or kidney-shaped; brown to yellowish brown; velvety; dry; the margin sometimes lobed or wavy; often bent at a sharp angle from the stem and thus reminiscent of the shape of Ganoderma lucidum. Pore Surface: White, becoming dingy or pinkish in age; terminating abruptly at the apex of the stem; tubes clearly discrete with a hand lens (see illustration); tubes to 5 mm long. Stem: Lateral; to 15 cm long; rooting and tapering to a basal point; dry; smooth; brownish, pinkish brown, or paler. The color of the stem near the apex reminds me of the liver-hued stem of Boletus separans. Flesh: White; fairly tough. Odor and Taste: Mild. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative on flesh. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 3-4 x 2-3 µ; smooth; broadly elliptical or subglobose; inamyloid. Cystidia absent. Hyphal system monomitic. REFERENCES: (Schweinitz, 1822) Burdsall, 1971. (Atkinson, 1901; Burdsall, 1971; Lincoff, 1992; Gilbertson & Ryvarden, 1986; Kuo & Methven, 2010.) Herb. Kuo 07130402. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2004, July). Pseudofistulina radicata. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/fistulina_radicata.html |