| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Collybioid > Gymnopus iocephalus |

|
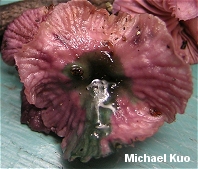
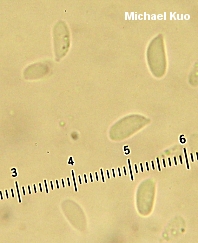
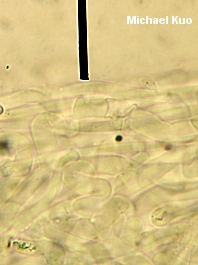
Gymnopus iocephalus [ Basidiomycetes > Agaricales > Marasmiaceae > Gymnopus . . . ] by Michael Kuo While a number of Gymnopus species turn green or olive when a drop of KOH is applied to their caps, Gymnopus iocephalus turns really green (sometimes even blue)--and the resulting contrast with the purple cap is stunning. The species appears to be primarily distributed in the southeastern United States, but it ranges north to Massachusetts and west to Missouri and Texas. Similar small, purple mushrooms include Laccaria amethystina (which features thickened gills and a cap that turns brownish with KOH), and Inocybe geophylla var. lilacina (with brownish mature gills and a brown spore print). Collybia iocephala is a synonym. Description: Ecology: Saprobic; growing scattered, gregariously, or in loose clusters on leaf or needle litter or from woody debris; summer and fall; distributed in the southeastern United States from Florida to Massachusetts, Missouri, and Texas. Cap: 1-2 cm; convex with an incurved margin when young, becoming broadly nearly flat, with an uplifted and wavy margin; moist or dry; bald; purple when young, fading to lilac or grayish lilac; the margin lined, sometimes nearly to the center. Gills: Narrowly attached to the stem, or nearly free from it by maturity; close or nearly distant; reddish purple. Stem: 2-5 cm long; 1-3 mm thick; more or less equal, or tapering to the apex; dry; finely velvety with whitish fuzz; purplish above and drab grayish or yellowish lilac below. Flesh: Pale lilac; thin. Odor and Taste: Odor not distinctive, or sometimes reported as reminiscent of gunpowder, garlic, or radish; taste unpleasant. Chemical Reactions: KOH green to blue on cap surface. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores: 6.5-8.5 x 3-4.5 µ; smooth; lacrymoid to ovoid; inamyloid. Pleuro- and cheilocystidia absent. Pileipellis a cutis of branched and interwoven elements 3-7.5 µ wide. REFERENCES: (Berkeley & M. A. Curtis, 1853) Halling, 1997. (Halling, 1983; Weber & Smith, 1985; Lincoff, 1992; Metzler & Metzler, 1992; Halling, 2004.) Herb. EIU ASM 9874. This website contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2013, February). Gymnopus iocephalus. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/gymnopus_iocephalus.html |