 Betula alleghaniensis (yellow birch) |
|
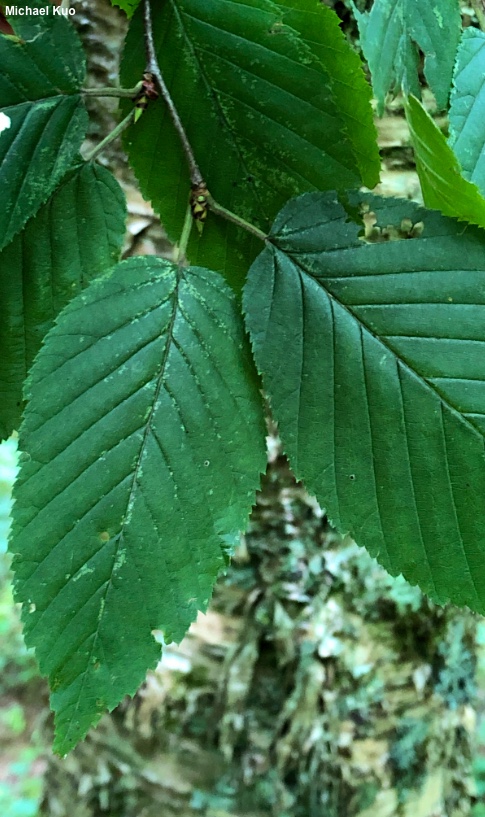
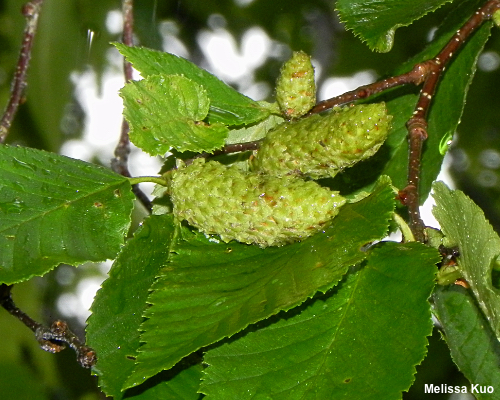
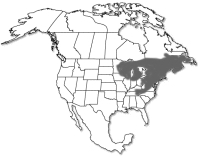
As its Latin name sugests, yellow birch is an Appalachian tree, although its range extends into northeastern North America and the northern Midwest; it is a central component of both northern hardwood and Appalachian cove forests. It is a fast growing tree, and a highly prolific seed producer; its seedlings do best in forest gaps caused by windthrow and other disturbances, where it is a colonizer. Identification of yellow birch is mostly a matter of assessing the color of the bark, which usually has yellowish tones. Like the bark of several other birch species, yellow birch bark is thin and papery, peeling in strips. However, the bark of paper birch is stark white, while the bark of river birch is pinkish to reddish, and these are the principal look-alike birches. Additionally, yellow birch can be separated by the many pairs of veins on its leaves (9–12); the only other birch with this many leaf veins is sweet birch, which does not have peeling bark. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
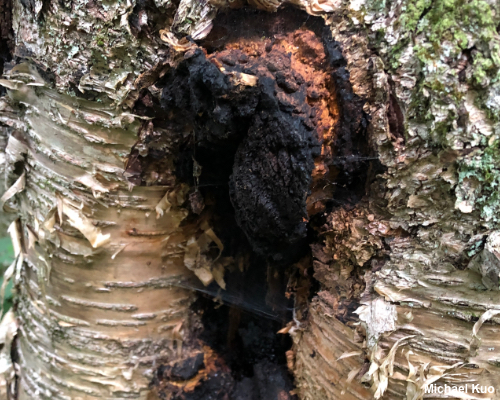
Frequent Mushroom Associates: Many mycorrhizal and saprobic mushroom species are associated with yellow birch. Parasitic mushrooms on yellow birch include Inonotus obliquus. Kuo, Michael (July, 2020). Betula alleghaniensis (yellow birch). Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.com website: www.mushroomexpert.com/trees/betula_alleghaniensis.html All text and images © , mushroomexpert.com. |





