| Major Groups > Gilled Mushrooms > Pale-Spored > Marasmioid > Marasmiellus candidus |

|
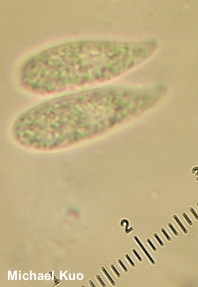
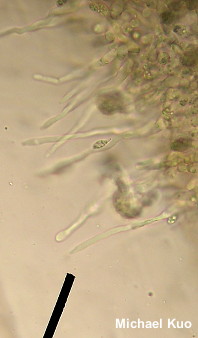
Marasmiellus candidus [ Basidiomycota > Agaricales > Marasmiaceae > Marasmiellus . . . ] by Michael Kuo Marasmiellus candidus is a tiny marasmioid mushroom found on sticks, canes, small logs, and similar forest litter. Originally named as a European species, it (or something very like it) appears to be widespread throughout North America, although it may be a bit more common on the West Coast than elsewhere on our continent. Distinguishing features include the habitat, the non-lined whitish cap, the very well-spaced gills, the whitish stem that becomes blackish from the base upward, and the tendency of older specimens to develop pinkish stains. Under the microscope, Marasmiellus candidus features large spores, filamentous cheilocystidia, and a pileipellis that lacks the funky, broom-cell-like "rameales" structures found in some other marasmioid species. Tetrapyrgos nigripes is very similar to the naked eye, but its gills are not quite as distant, and its stem base is inserted directly into the substrate (stick, leaf, etc.); the stem base of Marasmiellus candidus has a tiny pad of whitish fuzz at the point of attachment. Under the microscope the two species cannot be mistaken. Marasmius candidus, Marasmiellus albocorticis, and Marasmiellus albus-corticis are synonyms. Description: Ecology: Saprobic on twigs, canes, small logs, and similar litter in hardwood and conifer forests; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously; summer and fall, or over winter in warm climates; widely distributed in North America. The illustrated and described collections are from Illinois. Cap: 6–18 mm across; convex when young, becoming broadly convex with a central depression; thin and fragile; dry; bald; becoming slightly radially wrinkled, but not deeply lined or grooved; white to whitish; developing pinkish or yellowish stains with age. Gills: Running down the stem; very distant; becoming vein-like near the cap margin; developing cross-veins and short-gills; white; becoming pinkish with age. Stem: 4–7 mm long; 0.5–1 mm thick; equal; dry; at first bald and white, but usually developing a brownish gray to blackish tomentum from the base upward; with a small pad of whitish fuzz at the point of attachment to the substrate. Flesh: Thin; whitish; unchanging when sliced. Odor and Taste: Not distinctive. Chemical Reactions: KOH negative on cap surface. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 12–19 x 4–6 µm; more or less long-ellipsoid, with a stretched-out apicular end; smooth; hyaline and multiguttulate in KOH; inamyloid. Pleurocystidia absent. Cheilocystidia 50–100 x 2.5–5 µm; filiform to aciculate; apices subacute or merely rounded; smooth; thin-walled; hyaline in KOH. Pileipellis a cutis; elements 2.5–7.5 µm wide, smooth, hyaline, occasionally clamped, occasionally diverticulate. REFERENCES: (Fries, 1838) Singer, 1948. (Saccardo, 1887; Singer, 1973; Arora, 1986; Lincoff, 1992; Desjardin, 1997; Barron, 1999; Trudell & Ammirati, 2009; Antonín & Noordeloos, 2010; Desjardin, Wood & Stevens, 2015; Siegel & Schwarz, 2016.) Herb. Kuo 06211502. Herb. F WCG 2216. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2016, August). Marasmiellus candidus. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/marasmiellus_candidus.html |