| Major Groups > Saddles > Helvella dryophila |

|
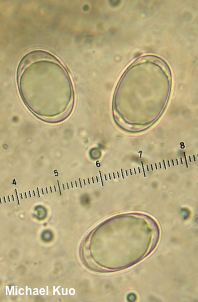
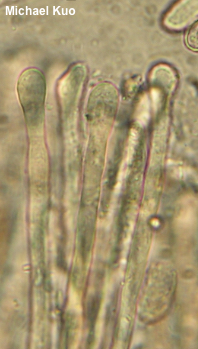
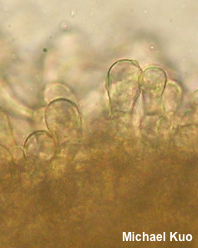
[ Ascomycota > Pezizales > Helvellaceae > Helvella . . . ] Helvella dryophila by Michael Kuo, 16 February 2024 Helvella dryophila is one of North America's many versions of Helvella lacunosa, recognized by its association with West-Coast oaks (especially coast live oak) in winter and spring. It is very similar to Helvella vespertina, which is associated with conifers and tends to appear in fall and winter, but the latter species often (not always, but often) reaches much larger proportions. Still, there is enough overlap in season and size that assessing the mycorrhizal host trees is your best bet for identification. Yes, West Coast ecosystems often contain both oaks and conifers, and yes, it can be virtually impossible to sort out probable mycorrhizal hosts. Ultimately, DNA sequencing may be the only "sure-fire" way to separate these species. Description: Ecology: Mycorrhizal with coast live oak and other oaks on the West Coast; growing alone, scattered, or gregariously; originally described from northern California (Vellinga & Nguyen 2013; the type collection was made on the the UC Berkeley campus); found from Oregon to southern California, eastward to the Sierra Nevada. The illustrated and described collections are from northern California. Cap: 1.5–4.5 cm across and 2–3.5 cm high; irregularly lobed and convoluted; black to dark gray; bald but wrinkled; the margin attached to the stem in several places; undersurface bald, gray to grayish brown. Stem: 3–5.5 cm long; 1–2.5 cm thick; more or less equal; grayish to dark gray, discoloring yellowish with age; deeply and ornately ribbed and pocketed; ribs with blunt edges; basal mycelium white. Flesh: Thin; brittle; chambered; whitish to grayish. Odor: Not distinctive. Microscopic Features: Spores 15–20 x 10–13 µm; broadly ellipsoid; smooth; with one oil large droplet; hyaline in KOH and in water. Asci 200–250 x 7.5–10 µm; 8-spored. Paraphyses 200–275 x 2.5–6 µm; filiform, with rounded to clavate, subcapitate, or irregularly swollen apices; smooth; hyaline to brown, often with granular contents. Excipular surface a palisade of clavate, hyaline to brown terminal elements 15–20 x 5–12.5 µm. REFERENCES: E. C. Vellinga & N. H. Nguyen, 2013. (Nguyen et al., 2013; Desjardin, Wood & Stevens, 2015; Landeros et al., 2015; Siegel & Schwarz, 2016; Skrede et al., 2017.) Herb. Kuo 02200310, 01191303, 01151503, 01142401. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2024, February). Helvella dryophila. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/helvella_dryophila.html |