| Major Groups > Jelly Fungi > Guepinia helvelloides |

|
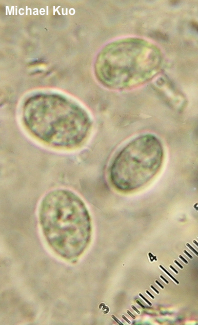
Guepinia helvelloides [ Basidiomycota > Auriculariales > Exidiaceae > Guepinia . . . ] by Michael Kuo This distinctive jelly fungus is hard to describe, but not so hard to recognize. Despite my usual cautions against identifying mushrooms by comparing them to photographs, I have to admit that Guepinia helvelloides is probably an exception. Look at the picture, add a semi-gelatinous consistency—and, well, that's Guepinia helvelloides. If you are worried about look-alikes, yank your putative Guepinia helvelloides hard as you pick it; if you hear screaming, you have pulled someone's tongue, and a little searching will probably reveal a human being concealed in the substrate. Phlogiotis helvelloides and Tremiscus helvelloides are synonyms. Description: Ecology: Saprobic; growing on the ground or on well-rotted wood; almost always found under conifers; summer and fall (also winter in warmer climates); originally described from France; widespread in Europe; widely distributed in North America but more common in the Northeast, the northern Midwest, Mexico, and the Pacific Northwest; also found in the Caribbean and in South America; reported (rarely) from Asia. The illustrated and described collection is from California. Fruiting Body: 2–5 cm high; with a confluent "cap" and "stem," though the dividing line between them is hard to pin down; "cap" funnel-shaped or irregular, often with a slit down one side; inner surface smooth, pinkish orange; outer surface smooth or wrinkled, colored like the inner surface (or paler); "stem" central or off-center, colored like the outer surface except for a whitish base; flesh rubbery. Odor and Taste: Not distinctive. Spore Print: White. Microscopic Features: Spores 10–11 x 5.5–7 µm; ellipsoid, with an apiculus; smooth; hyaline in KOH. Basidia longitudinally septate; ovoid; 4-sterigmate. Cystidia not found. Contextual hyphae 1–3 µm wide; smooth; sometimes gelatinizing; hyaline in KOH; clamp connections present. REFERENCES: (de Candolle, 1805) Fries, 1828. (Fries, 1822; Saccardo, 1888; Smith, 1949; Martin, 1952; Lowy, 1971; Smith, Smith & Weber, 1981; Arora, 1986; Breitenbach & Kränzlin, 1986; Phillips, 1991/2005; Lincoff, 1992; Barron, 1999; McNeil, 2006; Miller & Miller, 2006; Kuo & Methven, 2010; Buczacki et al., 2012; Siegel & Schwarz, 2016; Gminder & Böhning, 2017; Sturgeon, 2018; Læssøe & Petersen, 2019; McKnight et al., 2021.) Herb. Kuo 01120608. This site contains no information about the edibility or toxicity of mushrooms. |
© MushroomExpert.Com |
|
Cite this page as: Kuo, M. (2021, April). Guepinia helvelloides. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/Guepinia_helvelloides.html |